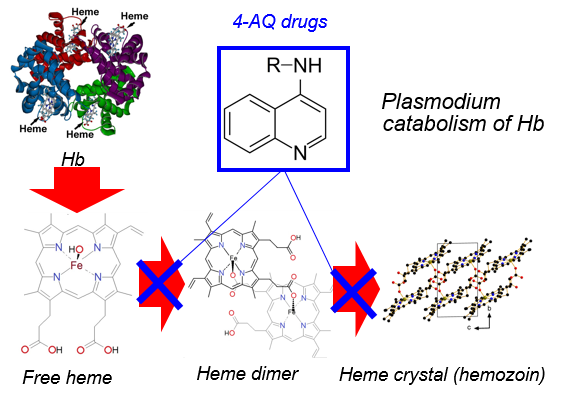
 Malaria is probably the topmost parasitic disease in terms of societal costs, as it causes thousands of deaths per year, especially in undeveloped coutries. The Plasmodium Falciparum protozoon infects human heritrocytes and digests the host emoglobin. This process releases free heme, which is toxic to the prarasite. Thus, free heme is deactivated by promoting its biocrystaliization into insoluble hemozoin crystals. 4-aminoquinoline antimalarials are believed to interfere with this detoxification pathway.
Malaria is probably the topmost parasitic disease in terms of societal costs, as it causes thousands of deaths per year, especially in undeveloped coutries. The Plasmodium Falciparum protozoon infects human heritrocytes and digests the host emoglobin. This process releases free heme, which is toxic to the prarasite. Thus, free heme is deactivated by promoting its biocrystaliization into insoluble hemozoin crystals. 4-aminoquinoline antimalarials are believed to interfere with this detoxification pathway.
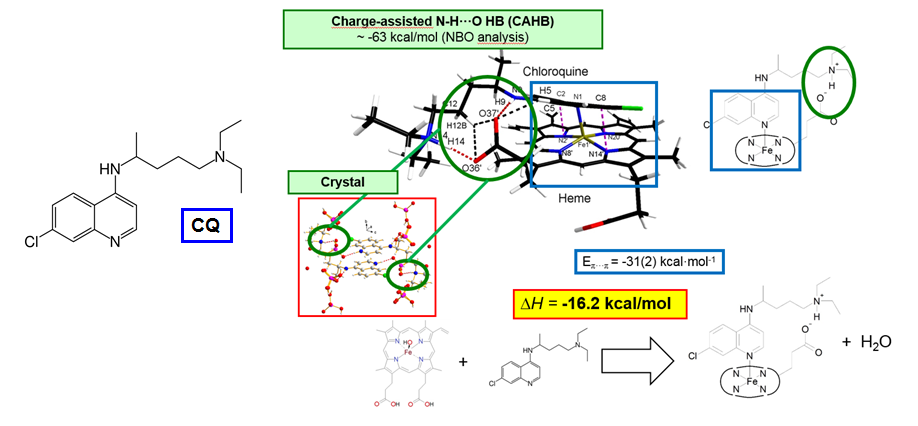
We are studying 4-aminoquinoline drugs, with main focus on chloroquine and piperaquine, with the aim of elucidating their heme-binding mechanism at the molecular level. On the basis of EXAFS and X-ray diffraction experiments, combined with quantum mechanical calculations, we discovered that a direct quinoline-heme interaction through a Fe-N coordinative bond is very probable.
Moreover, we demonstrated that the aliphatic amine is likely an active part of the drug pharmacophore, as it provides a significant part of the drug:substrate interaction energy by interacting with a propionate group of the Fe(III) protoporphyrin moiety. Unfortunately, chloroquine is no longer effective against P. Falciparum, as the parasite evolved specific resistance. Our idea is to take advantage of our experimental study of the drug pharmacophore to design cheap chemical derivatives that might restore its efficiency.
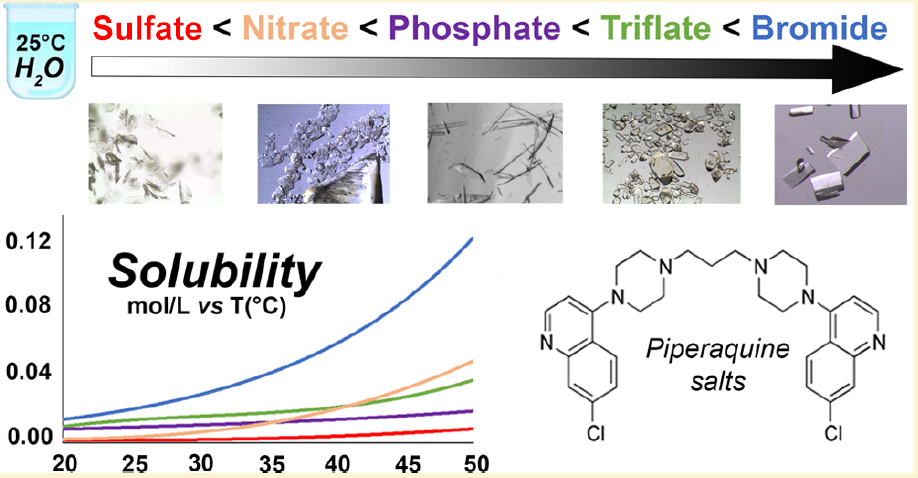
At the same time, we are studying alternative and more effective formulations of 4-aminoquinoline systems. Piperaquine is usually administred orally in an hydrogen phosphate tetrahydrate form, which is poorly soluble in water. We discovered that the solubility can be greatly improved by changing the counterion with softer anions.
Relevant publications:
Pietro Sacchi, Laura Loconte, Giovanni Macetti, Silvia Rizzato*, Leonardo Lo Presti*: Correlations of Crystal Structure and Solubility in Organic Salts: The Case of the Antiplasmodial Drug Piperaquine. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 1399-1410, DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.8b01794
Giovanni Macetti, Laura Loconte, Silvia Rizzato, Carlo Gatti, Leonardo Lo Presti*: Intermolecular Recognition of the Antimalarial Drug Chloroquine: A Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules–Density Functional Theory Investigation of the Hydrated Dihydrogen Phosphate Salt from the 103 K X-ray Structure. Crystal Growth & Design 09/2016; 16(10):6043–6054., DOI:10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01069
Giovanni Macetti, Silvia Rizzato, Fabio Beghi, Lucia Silvestrini, Leonardo Lo Presti*: On the molecular basis of the activity of the antimalarial drug chloroquine: EXAFS-assisted DFT evidence of a direct Fe–N bond with free heme in solution. Physica Scripta 02/2016; 91(2-2):023001., DOI:10.1088/0031-8949/91/2/023001
Research proposal: Lucia Silvestrini, Silvia Rizzato, Leonardo Lo Presti. Active lysosomal transport of 4-aminoquinoline alkaloids may provide new opportunities against SARS-CoV2. 2020. DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.24662.06721
