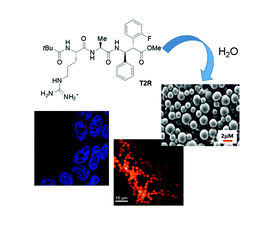
Self-assembly of an amphipathic ααβ-tripeptide into cationic spherical particles for intracellular delivery
The development of molecular carriers able to carry molecules directly into the cell is an area of intensive
research. Cationic nanoparticles are effective delivery systems for several classes of molecules, such as anticancer
agents, oligonucleotides and antibodies. Indeed, a cationic charge on the outer surface allows a
rapid cellular uptake together with the possibility of carrying negatively charged molecules. In this work, we
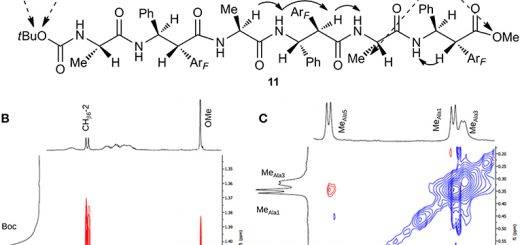
studied the self-assembly of an ultra-short ααβ-tripeptide containing an L-Arg–L-Ala sequence and an unnatural
fluorine substituted β2,3-diaryl-amino acid. The presence of the unnatural β2,3-diaryl-amino acid
allowed us to obtain a protease stable sequence. Furthermore, an arginine guanidinium group triggered the
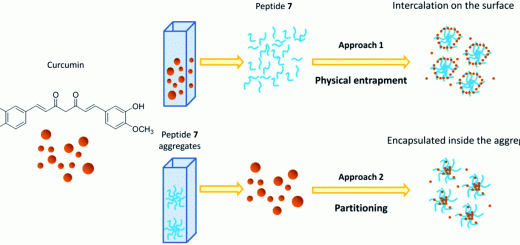
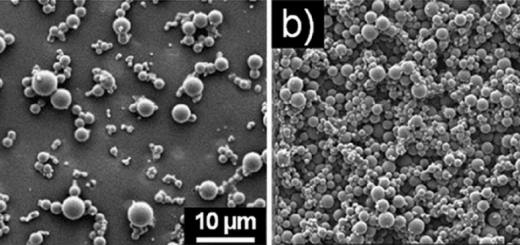
formation of spherical assemblies that were able to load small molecules and enter cells. These spherical
architectures, thus, represent interesting candidates for the delivery of exogenous entities directly into cells.




comments