Flow-Chemistry & catalytic reactors
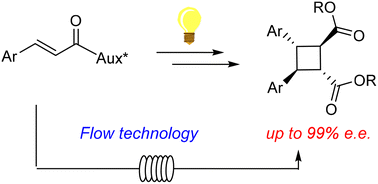
Stereoselective [2+2] Photodimerization: a Viable Strategy for the Synthesis of Enantiopure Cyclobutane Derivatives.
F. Medici, A. Puglisi, S. Rossi, L. Raimondi, M. Benaglia Org. Biomol. Chem., 2023 21, 2899-2904 [Link]
Abstract: The [2 + 2] photodimerization of cinnamic acid derivatives to afford enantiopure cyclobutanes has been investigated. The use of a chiral auxiliary
represents a convenient and straightforward method to exert enantiocontrol on the reaction. By exploiting Evans oxazolidinones, the stereoselective light-driven cyclisation
affords a functionalised cyclobutane ring with up to 99% enantiocontrol after removing the chiral auxiliary. In-flow experiments allowed us to improve further the efficiency
of the methodology, leading to high conversion and excellent enantioselectivity.
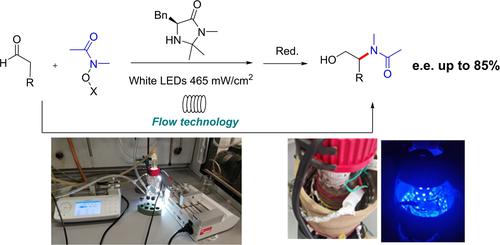
Enantioselective catalytic addition of N-acyl radicals: in batch and in flow organophotoredox α-amination of aldehydes
M. F. Boselli, N. Intini, A. Puglisi, L. Raimondi, S. Rossi, M. Benaglia Eur. J. Org. Chem, 2023 26, e2022013 [Link]
Abstract: The organophotoredox catalytic enantioselective addition of N-acyl radicals to aldehydes, to afford enantioenriched N-acyl 1,2 aminoalcohols was studied.
Under the best conditions, in batch, the product was isolated in up to 52% yield and 85% e.e., using a low cost and commercially available chiral imidazolidinone
as organocatalyst. The reaction was then studied in flow, exploring different experimental setups and photoreactors. Although modest yields were obtained, the in-flow process
afforded the product in higher productivities (up to 60 times higher) and improved space time yields (increased up to 113 times) compared to the batch reaction, with no
loss of stereoselectivity.
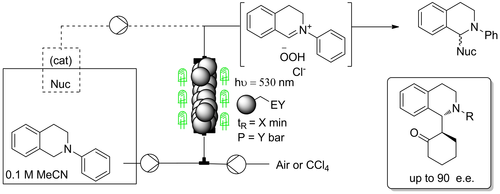
Immobilized Eosin Y for the photocatalytic oxidation of tetrahydroisoquinolines in flow
F. Herbrik, S. Rossi, M. Sanz, A. Puglisi, M. Benaglia Chemcatchem, 2022 [Link]
Abstract: A straightforward synthetic strategy for the immobilization of Eosin Y onto Merrifield-resin was successfully developed.
The easy-to-synthesize new material efficiently promoted the photooxidation of tertiary amines, especially operating with continuous flow catalytic reactors.
When using the iminium-ions in-situ or in a telescoped fashion the resulting Mannich-products could be isolated with high degrees of diastereo- and
enantioselectivity (up to 90% e.e.), simply using air as terminal oxidant. The same reactor was reused several times, with no loss of efficiency and no
apparent material degradation.
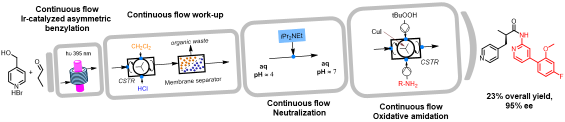
Enantioselective organophotocatalytic telescoped synthesis of a chiral privileged active pharmaceutical ingredient
F. Herbrik , M. Sanz, A. Puglisi, S. Rossi, M. Benaglia Chem. Eur. J., 2022 28 [Link]
Abstract: The continuous flow, enantioselective, organophotoredox catalytic asymmetric alkylation of aldehydes was studied, by using a homemade,
custom designed photoreactor for reactions under cryogenic conditions. Going from microfluidic conditions up to a 10 mL mesofluidic reactor, an increase
of productivity by almost 18000% compared to the batch reaction was demonstrated. Finally, for the first time, a stereoselective photoredox organocatalytic
continuous flow reaction in a fully telescoped process for an API synthesis was successfully achieved. The final process consists of 4 units of operation:
visible light-driven asymmetric catalytic benzylation under continuous flow, inline continuous work-up, neutralisation and a final oxidative amidation step
afforded the pharmaceutically active molecule in 95% e.e.
In-flow enantioselective homogeneous organic synthesis
A. Puglisi, S. Rossi, F. Herbrik, F. Medici and M. Benaglia Green Processing and Synthesis, 2021 10, 768-778 . [Link]
Abstract: The use of enabling technologies, such as flow reactors, three-dimensional-printed devices, and electrochemistry,
in the stereoselective synthesis of enantioenriched compounds is presented, with a special focus on the most
significant contributions to the field reported in the last few years.
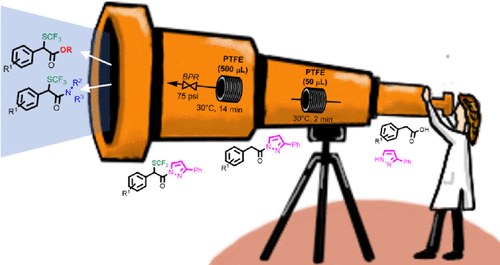
Continuous Flow Synthesis of α-Trifluoromethylthiolated Esters and Amides from Carboxylic Acids: a Telescoped Approach
F. Franco, S. Meninno, A. Lattanzi, A. Puglisi, M. Benaglia, J Org Chem, 2021 [Link]
Abstract: A continuous flow approach to access α-trifluoromethylthiolated esters and amides using commercially available arylacetic acids and
N-(trifluoromethylthio)phthalimide as the electrophilic reagent is described. The experimental protocol involves the in-flow conversion of the carboxylic acid into
N-acylpyrazole, followed by the α-trifluoromethylthiolation in a PTFE coil reactor and final reaction with primary or secondary amines, or alcohols,
to afford in a telescoped process -αsubstituted SCF3 amides and esters, respectively, in good overall yield and short reaction times.
Eosin Y: Homogeneous Photocatalytic In-Flow Reactions and Solid-Supported Catalysts for In-Batch Synthetic Transformations
F. Herbrik, P. Camarero González, M. Krstic, A. Puglisi, M. Benaglia, M.A. Sanz, S. Rossi Appl. Sci., 2020, 10, 5596 [Link]
Abstract: In this paper, the most recent and significant applications of Eosin Y as an organo-photocatalyst will be discussed, focusing the attention on enabling technological aspects in homogeneous photochemical flow reactions, as well as on recent developments in solid-supported catalyst applications for batch synthetic transformations.
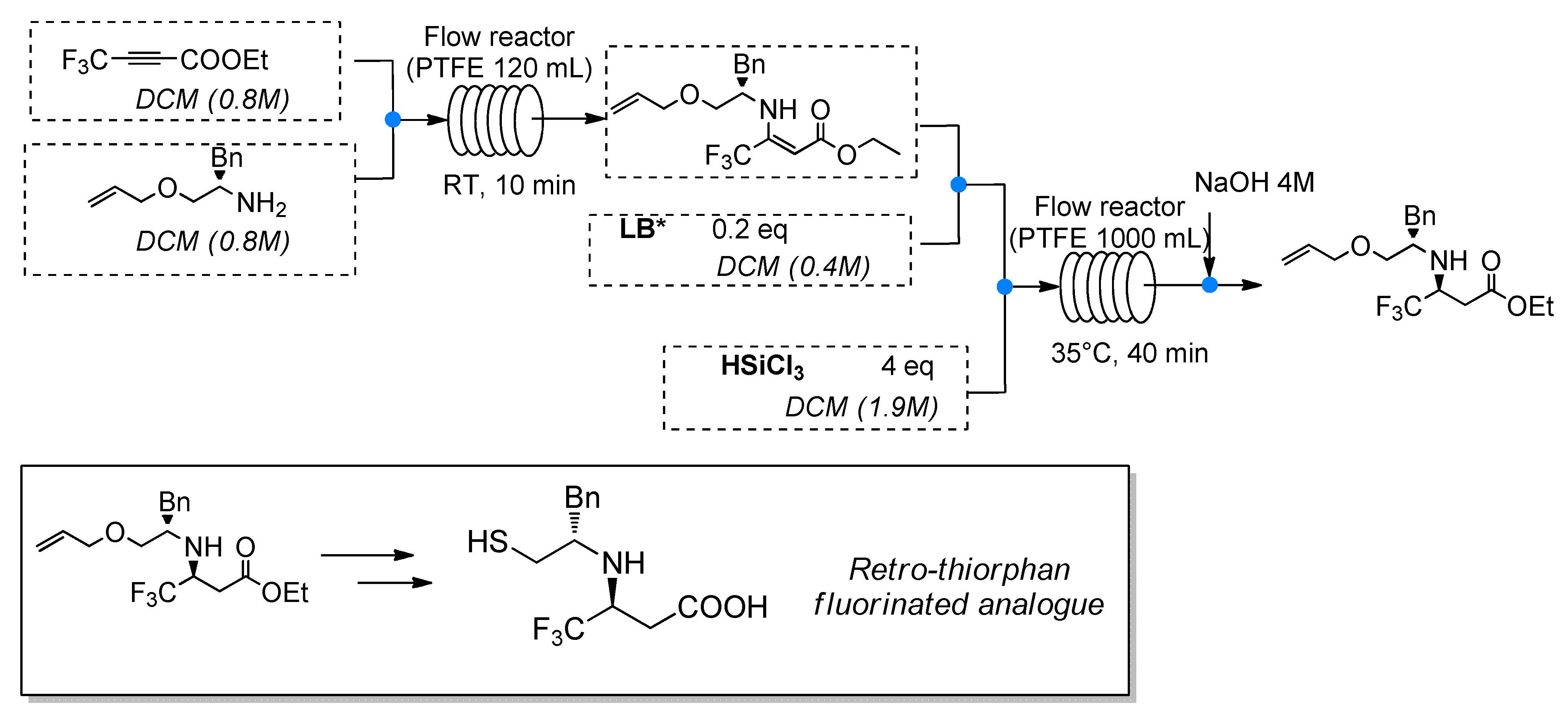
Evaluation of in-batch and in-flow synthetic strategies towards the stereoselective synthesis of a fluorinated analogue of retro-thiorphan
M. Pirola, A. Puglisi, L. Raimondi, A. Forni, M. Benaglia Molecules, 2019, 24 2260-2269 [Link]
.
Abstract: A stereoselective synthetic strategy for the preparation of trifluoromethylamine mimics of retro-thiorphan, involving a diastereoselective, metal-free catalytic step, has been studied in batch and afforded the target molecule in good yields and high diastereoselectivity. A crucial point of the synthetic sequence was the catalytic reduction of a fluorinated enamine with trichlorosilane as reducing agent in the presence of a chiral Lewis base. The absolute configuration of the key intermediate was unambiguously assigned by X-ray analysis. The synthesis was also investigated exploiting continuous flow reactions; that is, an advanced intermediate of the target molecule was synthesized in only two in-flow synthetic modules, avoiding isolation and purifications of intermediates, leading to the isolation of the target chiral fluorinated amine in up to an 87:13 diastereoisomeric ratio.
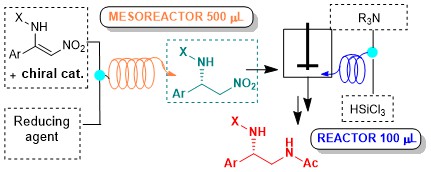
A continuous flow, two-steps, metal-free process for the synthesis of differently substituted chiral 1,2-diamino derivatives
M. Pirola, M. Benaglia, M. E. Compostella, L. Raimondi, A. Puglisi Synthesis, 2018, 50, 1430-1438 [Link]
.
Abstract: The enantioselective organocatalytic reduction of aryl-substituted nitroenamines was successfully performed under
continuous-flow conditions. After a preliminary screening with a 10 ul microreactor, to establish the best reaction conditions, the reduction
was scaled-up in a 0.5 ml mesoreactor, without appreciable loss of enantioselectivity, that remained constantly higher than 90%. The in-flow
nitro reduction was also accomplished, either by Raney-Ni catalyzed hydrogenation, and by a metal-free methodology based on the
use of the. very inexpensive and readily available reducing agent trichlorosilane. The final aim is to develop a two-step,
continuous-flow process for the stereoselective, metal-free, catalytic synthesis of differently functionalized chiral 1,2-diamines
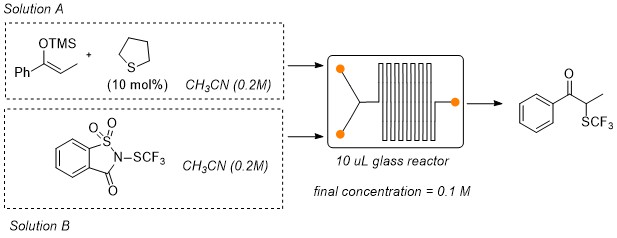
Organocatalytic α-trifluoromethylthiolation of silylenol ethers: batch vs continuous flow reactions
S. S. Abubakar, M. Benaglia, S. Rossi, R. Annunziata Cat. Today, 2017, accepted, doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2017.09.013 [Link]
Abstract: This work describes the organocatalytic a-trifluoromethylthiolation of silylenol ethers using N-(trifluoromethylthio)saccharin as
trifluoromethylthiolating reagent that is activated by the presence of catalytic amounts of a Lewis base. Tetrahydrothiophene was identified
as the best organocatalyst and it was successfully employed to promote the synthesis of different α-trifluoromethylketones; the reaction
has been performed under a traditional batch methodology and under continuous flow conditions. In general, yields obtained using the traditional
batch process were higher than those observed when the reaction was performed under flow conditions. However, short reaction times, higher
productivity and higher space time yields were observed when a flow system process was employed. Preliminary DFT calculations were also
performed in order to elucidate the mechanism of the reaction.
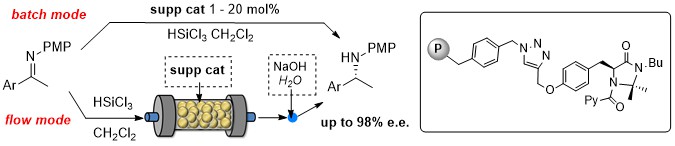
Solid supported chiral N-picolylimidazolidinones: recyclable catalysts for the enantioselective, metal- and H2-free reduction of imines in batch and in flow mode
R. Porta, M. Benaglia, R. Annunziata, A. Puglisi, G. Celentano Adv. Synth. Catal, 2017, 359, doi:10.1002/adsc.201700376 [Link]
Abstract: A new class of solid supported chiral imidazolidinones organocatalysts for the catalytic reduction of imines with trichlorosilane was developed. Polystyrene proved to be a more effective support than silica in terms of both chemical and stereochemical efficiency. Even with a loading as low as 1 mol % the best performing supported catalyst showed a remarkable activity and stereocontrol ability, promoting the reduction with stereoselectivities reaching 98% e.e. and in most cases ranging between 90-95% e.e. The general scope of the methodology and the good recyclability of the immobilized catalyst were demonstrated. The polystyrene-anchored chiral catalyst was also used to prepare packed bed reactors for the continuous flow synthesis of chiral amines, that were obtained in excellent yields and enantioselectivities. By exploiting the chiral organocatalytic reactor, the in-flow stereoselective synthesis of a common, immediate precursor of rivastigmine, of the calciomimetic (R)-NPS 568 and of Acrylamide (S)-A, currently under study for the treatment of neuropathic pain, was successfully accomplished.
Solid supported chiral N-picolylimidazolidinones: recyclable catalysts for the enantioselective, metal- and H2-free reduction of imines in batch and in flow mode
R. Porta, M. Benaglia, R. Annunziata, A. Puglisi, G. Celentano Adv. Synth. Catal, 2017, 359, doi:10.1002/adsc.201700376 [Link]
Abstract: A new class of solid supported chiral imidazolidinones organocatalysts for the catalytic reduction of imines with trichlorosilane was developed. Polystyrene proved to be a more effective support
than silica in terms of both chemical and stereochemical efficiency. Even with a loading as low as 1 mol % the best performing supported catalyst showed a remarkable activity and stereocontrol ability,
promoting the reduction with stereoselectivities reaching 98% e.e. and in most cases ranging between 90-95% e.e. The general scope of the methodology and the good recyclability of the immobilized catalyst
were demonstrated. The polystyrene-anchored chiral catalyst was also used to prepare packed bed reactors for the continuous flow synthesis of chiral amines, that were obtained in excellent yields and
enantioselectivities. By exploiting the chiral organocatalytic reactor, the in-flow stereoselective synthesis of a common, immediate precursor of rivastigmine, of the calciomimetic (R)-NPS 568 and of
Acrylamide (S)-A, currently under study for the treatment of neuropathic pain, was successfully accomplished.

Flow chemistry: recent developments in the synthesis of pharmaceutical products.
R. Porta, M. Benaglia, A. Puglisi Org. Process Res. Dev. , 2016, 20, 2-25 accepted
Abstract: In this review we focused our attention only on very recent advances in the continuous flow multistep synthesis of organic molecules which found application as APIs, especially highlighting the contributions
described in the literature from 2013 to 2015, including very recent examples not reported in any published review. Without claiming to be complete, we will give a general overview of different approaches,
technologies and synthetic strategies used so far, thus hoping to contribute to minimize the gap between academic research and pharmaceutical manufacturing. A general outlook about a quite young and relatively
unexplored field of research, like stereoselective organocatalysis under flow conditions will be also presented, and most significant examples will be described; our purpose is to illustrate all the potentialities
of continuous flow organocatalysis and offer a starting point to develop new methodologies for the synthesis of chiral drugs. Finally, some considerations on the perspectives and the possible, expected developments
in the field are briefly discussed.
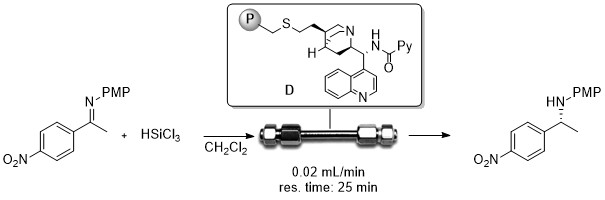
Stereoselective Reduction of Imines with Trichlorosilane using Solid-Supported Chiral Picolinamides
S. D. Fernandes, R. Porta, P. C. Barrulas, A. Puglisi, A. J. Burke, M. Benaglia Molecules, 2016, 21, (9), 1490-1499. [Link]
Abstract: The stereoselective reduction of imines with trichlorosilane catalyzed by chiral Lewis bases is a well-established procedure for the synthesis of enantio-enriched amines. Five supported cinchona-based picolinamides have been prepared and their activity tested in a model reaction. The comparison of different supporting materials revealed that polystyrene gave better results than silica in terms of stereoselectivity. The applicability of the solid-supported catalyst of choice to the reduction of different imines was also demonstrated. Additionally, for the first time a catalytic reactor containing a polymer-immobilized chiral picolinamide has been employed for the stereoselective reduction of imines with trichlorosilane under continuous flow conditions.
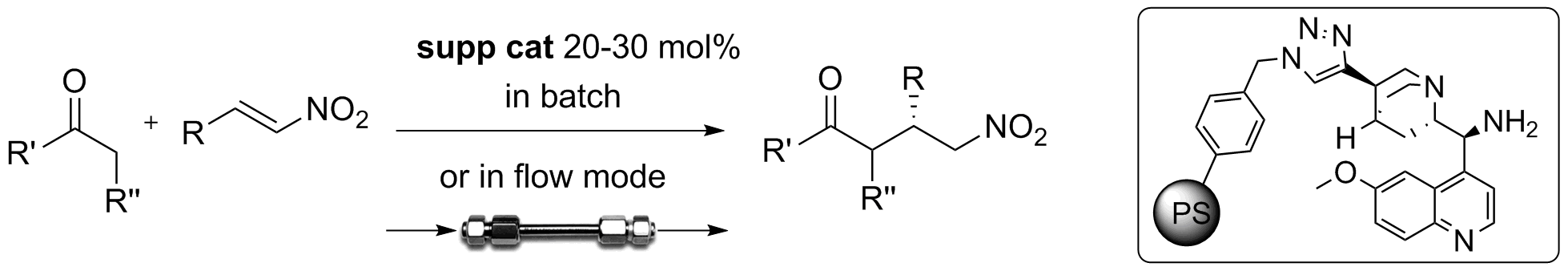
Solid supported 9-amino-9-deoxy-epi-quinine as efficient organocatalysts for stereoselective reactions in batch and under continuous flow conditions.
R. Porta, M. Benaglia, F. Coccia, F. Cozzi, A. Puglisi Adv. Synth. Catal , 2015, 357, 377-383 [Link]
Abstract: Polystyrene supported 9-amino-9-deoxy-epi-quinine was synthesized through co-polymerization of an ad hoc-designed chiral monomer with divinylbenzene, in the presence of AIBN as radical
initiator and toluene and 1-dodecanol as porogenic solvents. The heterogenized catalyst efficiently promoted the reaction of i-butyric aldehyde with β-nitrostyrene, in very
high yield and enantioselectivity, comparable or even higher than that of the homogeneous counterpart (up to 95% ee). The recyclability of the catalyst, its general applicability and its
successful application to other reactions was also demonstrated. Finally, for the first time, a 9-amino-epi-quinine derivative was employed to perform an enantioselective Michael
reaction under continuous-flow conditions; by using a home-made, packed-bed catalytic reactor, the aldehyde.
Comparison of Different Polymer- and Silica-Supported 9-Amino-9-deoxy-epi-quinines as Recyclable Organocatalysts.
R. Porta, F. Coccia, R. Annunziata and A. Puglisi, ChemCatChem, 2015, 7, 1490-1499. [Link]
Abstract:9-Amino-9-deoxy-epi-quinine, properly modified by suitable linkers, was anchored on highly cross-linked polystyrene, poly(ethylene glycol), and silica. The resulting species were characterized by NMR spectroscopy and tested as supported organocatalysts in the reaction between isobutyric aldehyde and trans-߭nitrostyrene. Polystyrene- and poly(ethylene glycol)-supported catalysts outperformed their nonsupported counterpart affording the desired product in high yield and ee (>90% ee). Silica-supported catalysts proved to be less efficient in terms of both chemical yield and enantioselectivity. Polystyrene- and poly(ethylene glycol)-supported 9-amino-9-deoxy-epi-quinine were then used in the same reaction with different substrates, leading to the desired products in high yield and ee, as well as in three other reactions operating with different mechanism. An investigation of the recyclability of the polystyrene- and poly(ethylene glycol)-supported systems showed that these could be recovered and recycled with no loss of stereochemical activity but with a marked erosion of chemical efficiency occurring at the fifth reaction cycle. This was ascribed to chemical degradation of the alkaloid occurring during the reaction.
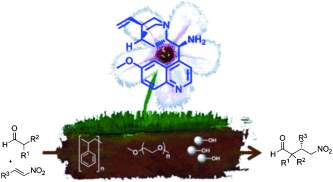
A catalytic reactor for organocatalyzed enantioselective continuous flow alkylation of aldehydes
R. Porta, M. Benaglia, A. Puglisi, A. Mandoli, A. Gualandi, P.G. Cozzi ChemSusChem , 2014, 7, 3534-3540. [Link]
Abstract: The use of immobilized metal-free catalysts offers the unique possibility to develop sustainable processes in flow mode. A challenging transformation like the intermolecular
organocatalyzed aldehyde enantioselective alkylation was performed for the first time under continuous flow conditions. By using a packed-bed catalytic reactor filled with readily
available and relatively inexpensive solid-supported enantiomerically pure imidazolidinone, different aldehydes were reacted with three distinct cationic electrophiles. In the
organocatalyzed α-alkylation of aldehydes with 1,3-benzodithiolylium tetrafluoroborate excellent enantioselectivities, in some cases even better than in the flask process
(up to 95% e.e. at 25 °C) and high productivity (more than 3800 h-1) were obtained, thus showing that the catalytic reactor may efficiently work and continuously produce enantiomerically
enriched compounds. The treatment of the alkylated products with Raney Nickel allows to obtain enantiomerically enriched α-methyl derivatives, key intermediates for the production
of APIs and natural products.
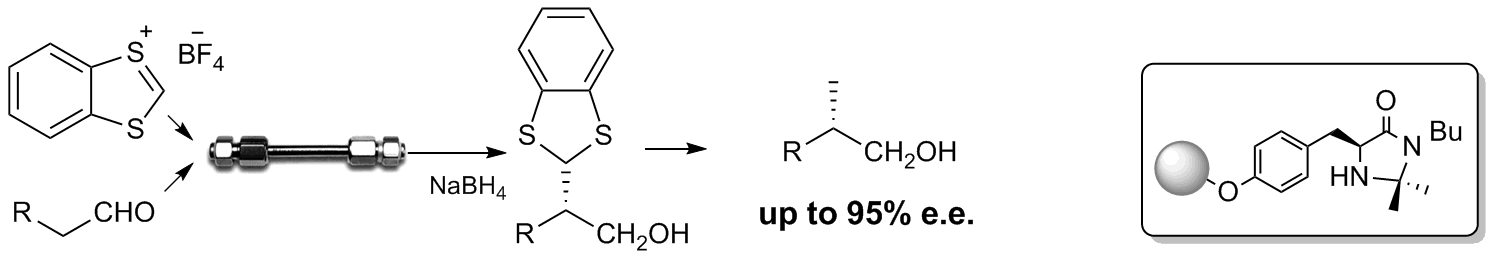
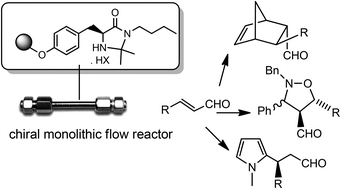
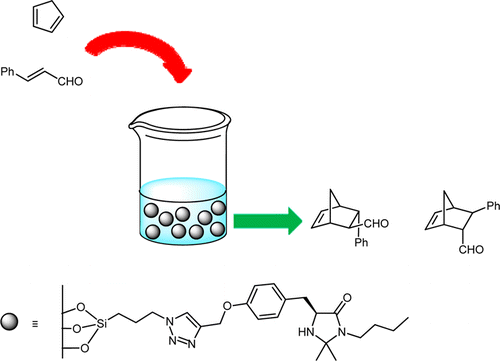
A chiral organocatalytic polymer-based monolithic reactor
V. Chiroli, M. Benaglia, A. Puglisi, R. Porta, R. P. Jumde, A. Mandoli Green Chem, 2014, 16, 2798-2806. [Link]
Abstract: Radical copolymerisation of divinylbenzene and a properly modified enantiomerically pure imidazolidinone inside a stainless steel column in the presence of dodecanol and toluene as
porogens afforded the first example of a chiral organocatalyst immobilized onto a monolithic reactor. Organocatalyzed cycloadditions between cyclopentadiene and cinnamic aldehyde
were performed under continuous-flow conditions; by optimizing the experimental set up, excellent enantioselectivities (90% ee at 25 у) and high productivities (higher than 330) were
obtained, thus showing that a catalytic reactor may work efficiently to continuously produce enantiomerically enriched compounds. The same catalytic reactor was also employed to carry
out three different stereoselective transformations in continuo, sequentially, inside the chiral column (Diels-Alder, 1,3-dipolar nitrone-olefin cycloaddition, and Friedel-Crafts
alkylation); excellent results were obtained in the case of the former two reactions (up to 99% yield, 93% ee and 71% yield, 90% ee, at 25у, respectively). In addition to simplify
the product recovery, the monolithic reactor performed better than the same supported organocatalyst in a stirred flask and could be kept working continuously for more than 8 days.
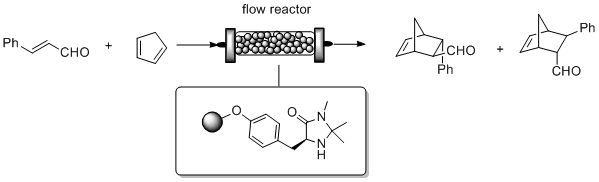
Stereoselective Diels-Alder reactions promoted under continuous-flow conditions by silica supported chiral organocatalysts
R. Porta, M. Benaglia, V. Chiroli, F. Coccia, A. Puglisi Isr. J. Chem., 2014, 54, 381-394. [Link]
Abstract: Silica nanoparticles of different morphological properties were functionalized with enantiomerically pure imidazolidinones, through different immobilization techniques;
stainless steel columns were then loaded with silica bearing the chiral organocatalysts, to realize chiral “homemade” reactors. The influence of the material properties
and of the immobilization procedures on the chemical and stereochemical activities of the chiral HPLC columns was studied, by performing organocatalyzed Diels-Alder
reactions under continuous-flow conditions between cyclopentadiene and α,β-unsaturated aldehydes. In some cases, excellent enantioselectivities were obtained, thus showing
that a catalytic reactor may work efficiently to continuously produce enantiomerically enriched cycloadducts for more than 200 hours. The regeneration of the organocatalytic
column was also partially accomplished, although associated with a slightly lower enantioselectivity, thus prolonging the “life” of the reactor to more than 300 hours.
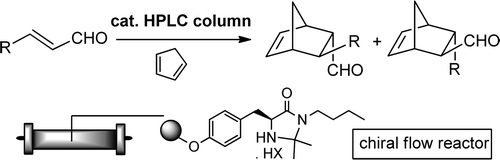
Continuous-Flow Stereoselective Organocatalyzed Diels-Alder Reactions in a Chiral Catalytic "Homemade" HPLC Column
V. Chiroli, M. Benaglia, F. Cozzi, A. Puglisi, R. Annunziata, G. Celentano Org. lett., 2013, 15,3590-3593. [Link]
Abstract: Continuous-flow organocatalyzed Diels-Alder reactions have been performed with excellent enantioselectivity for the first time in a chiral “homemade” HPLC column, packed with
silica on which a MacMillan catalyst has been supported by a straightforward immobilization procedure. The versatility of the system was also proven by running with the same
column continuous-flow stereoselective reactions with three different substrates, showing that the catalytic reactor may efficiently work in continuo for more than 150 h;
the regeneration of the HPLC column was also demonstrated, allowing to further extend the activity of the reactor to more than 300 operating hours.
Stereoselective organic reactions promoted by immobilized chiral catalysts in continuous flow systems
A. Puglisi, M. Benaglia, V. Chiroli Green Chemistry, 2013, 15, 1970-1813. [Link]
Abstract: The immobilization of the catalyst on a support with the aim of facilitating the separation of the product from the catalyst,
and thus the recovery and recycling of the latter, can be regarded as an important improvement for a catalytic process. However,
a system where a catalyst must not be removed from the reaction vessel is even more attractive: in continuous flow methods the
immobilized catalyst permanently resides in the reactor where it transforms the entering starting materials into the desired products. The
retention of the catalytic species inside the reaction vessel can be achieved by different techniques ranging from ultrafiltration through
a MW-selective membrane to immobilization on different supports. In this review we will discuss the most significant examples of stereoselective
reactions promoted by immobilized chiral catalysts and performed under continuous flow conditions, with particular attention to the more recent
contributions of the last few years.
Chiral Hybrid Inorganic - Organic Materials: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application in Stereoselective Organocatalytic Cycloadditions.
A. Puglisi, M. Benaglia, R. Annunziata, V. Chiroli, R. Porta, A. Gervasini J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78, 11326-11334. [Link]
Abstract: The synthesis of chiral imidazolidinones on mesoporous silica nanoparticles, exploiting two different anchoring sites and two different linkers, is reported. Catalysts 1-4 were prepared starting from L-phenylalanine or L-tyrosine methyl esters and supporting the imidazolidinone onto silica by grafting protocols or azide-alkyne copper(I)-catalyzed cycloaddition. The four catalysts were fully characterized by solid-state NMR, N2 physisorption, SEM,and TGA in order to provide structural assessments, including an evaluation of surface areas, pore dimensions, and catalyst loading. They were used in organocatalyzed Diels-Alder cycloadditions between cyclopentadiene and different aldehydes, affording results comparable to those obtained with the nonsupported catalyst (up to 91% yield and 92% ee in the model reaction between cyclopentadiene and cinnamic aldehyde). The catalysts were recovered from the reaction mixture by simple filtration or centrifugation. The most active catalyst was recycled two times with some loss of catalytic efficiency and a small erosion of ee.
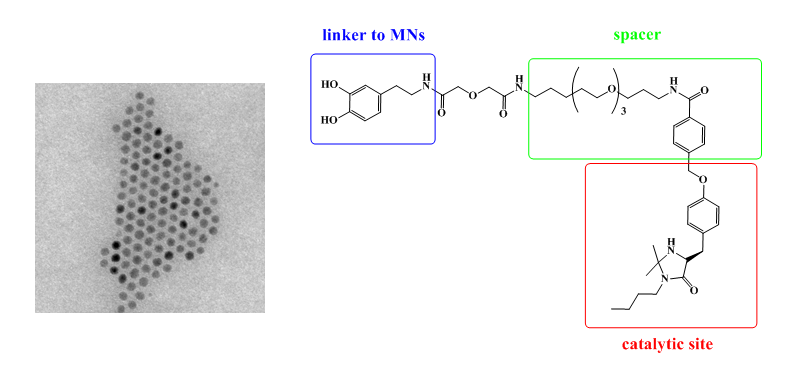
Magnetic nanoparticles conjugated to chiral imidazolidinone as recoverable catalyst.
S. Mondini, A. Puglisi, M. Benaglia, D. Ramella, C. Drago, A. M. Ferretti, A. Ponti, Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2013, 15, 2025-2036. [Link]
Abstract: The immobilization of an ad hoc designed chiral imidazolidin-4-one onto iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) is described, to afford MNPsupported MacMillan's catalyst. Morphological and structural analysis of the materials, during preparation, use, and recycle, has been carried out by transmission electron microscopy. The supported catalyst was tested in the Diels-Alder reaction of cyclopentadiene with cinnamic aldehyde, affording the products in good yields and enantiomeric excesses up to 93%, comparable to those observed with the non-supported catalyst. Recovery of the chiral catalyst has been successfully performed by simply applying an external magnet to achieve a perfect separation of the MNPs from the reaction product. The recycle of the catalytic system has been also investigated. Noteworthy, this immobilized MacMillan's catalyst proved to be able to efficiently promote the reaction in pure water.
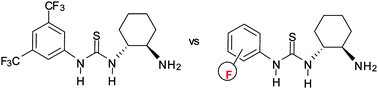
Synthesis and catalytic activity of fluorous chiral primary amine-thioureas.
S. Orlandi, G. Pozzi, M. Ghisetti, M. Benaglia, New J. Chem., 2013, 37, 4140-4147. [Link]
Abstract: Three enantiopure fluorous thioureas featuring a free H2 group were synthesized by direct addition of aromatic isothiocyanates bearing a single n-C8F17 substituent in the ortho, meta and para position, respectively, to enantiopure (1R,2R)-1,2-diaminocyclohexane. The catalytic behavior of these bifunctional molecules was assessed in representative Michael-type reactions. The three fluorous thioureas performed similarly in all the reactions tested, thus showing that the position of the fluorous ponytail does not have a major influence on the catalytic behavior of this class of compounds. In particular, excellent enantioselectivities (up to 99% ee) and yields (up to 98%) were obtained for the addition of aliphatic aldehydes to maleimides to give a-substituted succinimides. Recyclability of these primary amine-based thioureas was found to be limited by the concurrent formation of imine-derivatives during the catalytic process, leading to a structural modification of the organic catalyst.
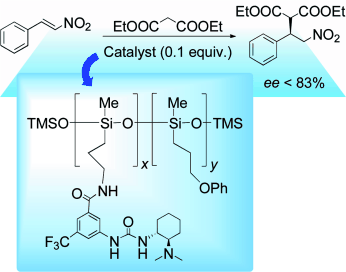
Immobilization of Chiral Bifunctional Organocatalysts on Poly(methylhydrosiloxane).
A. Puglisi, M. Benaglia, R. Annunziata, J. S. Siegel, Chem. Cat. Chem., 2012, 48, 3188-3190. [Link]
Abstract: Takemoto promotes: Enantiomerically pure bifunctional chiral catalysts are immobilized on poly(methylhydrosiloxane). A supported Takemoto-type catalyst promoted the diethyl malonate addition to nitrostyrene in fair to good yields and up to 83% ee, and its recyclability is demonstrated.
Hybrid inorganic-organic materials carrying tertiary amine and thiourea residues tethered on mesoporous silica nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and cooperative catalysis.
A. Puglisi, R. Annunziata, M. Benaglia, F. Cozzi, A. Gervasini, V. Bertacche, M. C. Sala, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2009, 351, 219-229. [Link]
Abstract: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles carrying different loadings of tertiary amine and thiourea residues (residues ratios 53/47, 68/32, and 22/78, respectively) were synthesized by the co-condensation method and fully characterized by CP MAS NMR, powder XRD, SEM, BET, BJH and FT-IR techniques. These materials were tested as bifunctional catalysts in the conjugate addition of acetylacetone to 2-nitrostyrene, a reaction that under solvent-free conditions occurred in quantitative yield. By carrying out several experiments with the bifunctional catalysts featuring different molar ratios of active sites, and with different combinations of monofunctional supported and non-supported catalyst, the co-operativity of the tertiary amine and thiourea residues in catalyzing the reaction was demonstrated. The use of the bifunctional catalyst was extended to the addition of acetylacetone to an activated imine. Catalyst recycling for a total of three reaction cycles was demonstrated without significant erosion of activity.
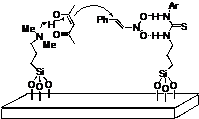
Book chapter: Recoverable organic catalysts
M. Benaglia,ed. John Wiley and Sons, Recoverable and Recyclable Catalysts, 2009 [Link]