Material chemistry
Set-Up of Bacterial Cellulose Production From the Genus Komagataeibacter and Its Use in a Gluten-Free Bakery Product as a Case Study.
I. Vigentini, V. Fabrizio, F. Dellaca, S. Rossi, I. Azario, C. Mondin, M. Benaglia, R. Foschino Frontiers In Microbiology, 2019, 10, 1953-1963 [Link]
Abstract:The use of bacterial cellulose (BC) in food systems is still limited due to production costs. Nine clones belonging to Komagataeibacter hansenii, Komagataeibacter nataicola, Komagataeibacter rhaeticus, Komagataeibacter swingsii, and Komagataeibacter xylinus species were screened for cellulose productivity in growth tests with five different carbon sources and three nitrogen sources. The water-holding and rehydration capacities of the purified cellulose were determined. The structure of the polymer was investigated through nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FT-IR) spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, and observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Natural mutants of K. rhaeticus LMG 22126T and K. swingsii LMG 22125T showed different productivity. The factors “bacterial isolate” and “nitrogen source” significantly affected the production of cellulose (p < 0.01) rather than the factor “carbon source” (p = 0.15). However, on average, the best conditions for increasing yield were found in medium containing glucose and peptone. Water-holding capacity (WHC) values ranged from 10.7 to 42.3 (gwater/gcellulose) with significant differences among strains (p < 0.01), while the rehydration capacity varied from 4.2 to 9.3 (gwater/gcellulose). A high crystallinity (64–80%) was detected in all samples with Iα fractions corresponding to 67–93%. The ATR-FT-IR spectra and the XRD patterns confirmed the expected structure. BC made by GVP isolate of K. rhaeticus LMG 22126T, which was the strain with the highest yield, was added to a gluten-free bread formulation. Results obtained from measurements of technological parameters in dough leavening and baking trials were promising for implementation in potential novel foods
Easily Available, Low Cost 19F-MRI Agents: Poly(ethylene-glycol)-functionalized Fluorinated Ethers.
C. Biaggi, M. Benaglia, M. Ortenzi, E. Micotti, C. Perego,M. G. De Simoni Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2013, 153,172-177 [Link]
Abstract: Poly(ethylene-glycol) derivatives of different fluorine content were easily synthesized. In all cases a single 19F signal at NMR in deuterated chloroform and D2O was registered; in a few cases a good solubility in water was observed and a clear imaging was obtained in experiments of in vitro MR imaging. In one case a novel fluorinated polymer was tolerated in low doses when in vivo experiments on animals (mice) were conducted.
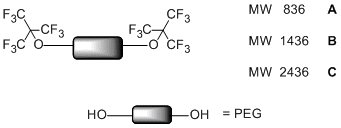
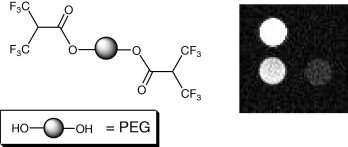
Poly(ethylene-glycol)-based Fluorinated Esters: a Readily Available Entry for Novel 19F-MRI agents
S. Rossi, M. Benaglia, M. Ortenzi, E. Micotti, C. Perego, M. G. De Simoni, Tetrahedron Lett., 2011, 52, 6581-6583. [Link]
Abstract: Readily available, low cost, hydrosoluble poly(ethylene-glycol) derivatives of 2-(trifluoromethyl)-3,3,3-trifluoro-propanoic acid were easily synthesized and their properties as MRI agents are preliminarily investigated. Two novel polymers, of 2356 Da and 756 Da, respectively, both showing a single 19F signal at NMR in deuterated chloroform and D2O were fully characterized; both compounds were shown to be soluble in water. However when experiments of in vitro MR imaging were conducted a clear imaging was obtained only with the sample of 756 MW, pointing at the importance of the fluorine content of the carrier..